How Thermal Printers Work: An In-Depth Guide
If you’re considering investing in a thermal printer, it’s always a good idea to know how they work – after all, they can provide quick, reliable printing while saving time and money. In this post, you’ll get an in-depth look under the hood of thermal printers and find out exactly how they work and why they’re so popular. From their construction and components to the process of printing itself, we’ll cover everything you need to know about thermal printers, so you can decide if they are the right fit for your needs. So, let’s clear the air, roll up our sleeves and get to work learning everything there is to know about thermal printers.
Thermal Printers are popular technologies in today’s world. Most modern businesses rely on them and the best small printers to produce the wide variety of data and documents they need. Thermal printers come in various styles, configurations, and sizes, and can contain a multitude of features. Understanding how these specialized printing machines work is essential for any business seeking to utilize their capabilities successfully. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of how thermal printers function and operates, providing readers with a comprehensive overview of the technology involved in their creation. We’ll begin by taking a look into what thermal printers are and how they’ve been used throughout history. We’ll then explore different components integral to all thermal printing machines, such as thermal paper, print heads, and control boards. To conclude this introduction, we’ll briefly consider what other types of printing mechanisms share many similarities with thermal printers. With our introductory section now complete, it’s time to move on to provide an overview of the printing technology used by thermal printers. This will include details on the three distinct processes that dominate the thermal printing industry – direct thermal printing, dye-sublimation sublimation, and laser transfer printing – as well as other topics related to their mechanisms for reproducing images on paper. With this knowledge in hand, we’ll be well-equipped to dive deeper into the specifics of how each process works when we start looking at individual models of specific printers in later sections.
Overview of Printing Technology
Having a basic understanding of thermal printing technology is essential for any professional or consumer looking to print documents quickly and efficiently. However, not all thermal printers are the same. As technology has advanced, methods have been developed that offer improved features and capabilities over traditional thermal printing. This section will provide an overview of some of the most popular printing technologies, contrasting their advantages and disadvantages. Dot-matrix technology remains one of the oldest and still widely used thermal printing methods. It uses a small plastic ribbon to create images on paper by pressing tiny pins against it in rapid succession. A typical attribute of dot-matrix thermal printing is its low cost and high speed, but its lack of image quality makes it impractical for many applications. As an alternative, thermal transfer printing utilizes a heat source along with wax or resin-based ribbons to generate images on paper or other materials. This process offers higher quality results than dot-matrix and is a great solution if you’re looking for sharp text or graphics. The primary downside to this type of printing is that it can be slow and costly due to its reliance on specialty ink materials. Finally, another option available is direct thermal printing, which relies solely on heat-sensitive paper to create images without using ribbons. While direct thermal printers are usually slower than other methods, they offer quick relief when compared to more expensive options and deliver decent-quality output at lower costs. It’s important to keep in mind that each method offers something different; whether it’s speed, convenience, or cost efficiency. With such a diverse array of products available, it is critical to review your needs carefully so that you find the right solution for your specific application. In the next section, we’ll take an in-depth look into how these various methods actually work.
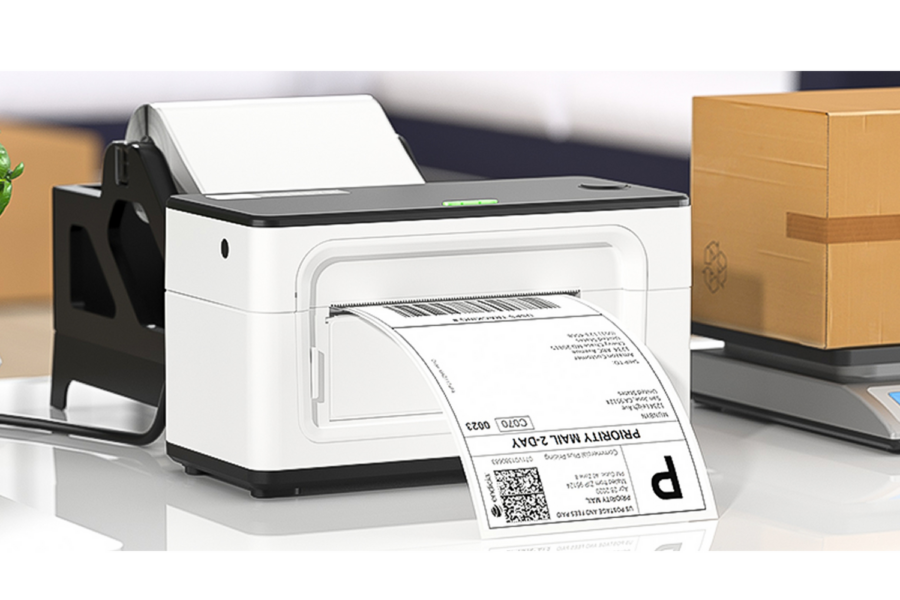
How Thermal Printers Work?
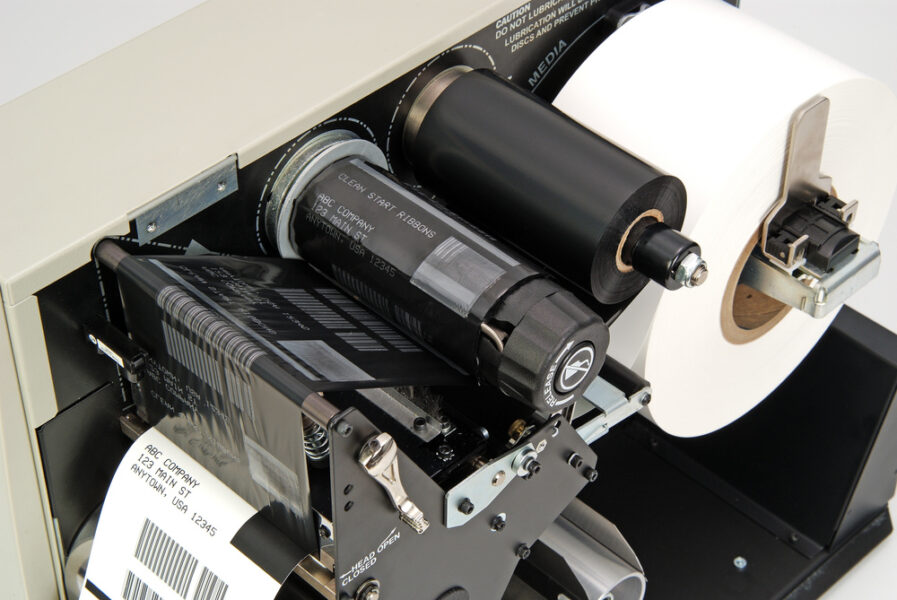
Source: thermallabelwarehouse.com
Thermal printers are specialized machines that utilize heat to print documents on thermal paper or other substrates. Thermal printing is one of the most widely used printing technologies in the world, with a variety of thermal printer models to choose from. To better understand how these machines work, it’s important to have an understanding of the main components that make up a thermal printer, such as its print head and ribbon materials. The print head is largely responsible for an accurate print job. In thermal printers it contains an array of tiny pins heated by electrical current, allowing them to create words and images on various substrates. The ribbon material also plays an important role since this is what melts onto the substrate and leaves behind the desired design or text. Different kinds of ribbons are available depending on the particular needs of the application, such as heat transfer ribbons, wax/resin ribbons, and dye-sublimation ribbons. It’s worth noting that thermal printing technology has some advantages over other printing methods; for example, prints produced by thermal printers generally last longer than other types of prints due to their durability and resistance against fading. Additionally, these machines don’t require costly supplies like ink or toner cartridges as they use heat instead. However, it’s important to keep in mind that this technology isn’t suitable for all applications—prints created with a thermal printer may be smudged if exposed to too much humidity or heat. Ultimately, understanding how thermal printers work requires knowledge about the various components involved and their function during the printing process – something that will be further discussed in the following section.
- Thermal printers use heat to transfer ink onto paper.
- Thermal printing technology is typically used for small-format printing jobs like receipts, labels, and tickets.
- According to Statista, nearly 30 percent of all global POS systems have adopted thermal printing technology as of 2019.
The Process of Printing
The process of printing with thermal printers is surprisingly fast and efficient. When a document is sent to the printer, a thermally sensitive dye-coated paper is advanced through the printer and exposed to tiny pins that heat up almost instantly. As these pins move across the paper, they can produce letters, symbols, and graphics. Generally, this printing process starts from one end of the printer and moves across a continuous roll of paper until the desired document has been printed on the sheet. The entire process only takes milliseconds to run through, which is incredibly faster than inkjet or laser printers. Thermal printers also require less maintenance because there’s no need for ink cartridges or toner replacements. All you need to do is make sure you have enough thermally sensitive paper to keep your printer rolling! On the flip side, thermal printers are limited in what type of printing they can effectively manage. For example, thermal printers don’t allow for high-quality image printing or custom colors and shades. This is because they work by burning paper, which requires relatively high temperatures to generate printing results. If you’re looking for numerous colors and the highest printing quality possible, then a laser or inkjet printer would be more suitable. Overall, however, thermal printers deliver much-needed speed and convenience when quickly producing simple documents with black text or basic graphics. This makes them ideal for applications such as point-of-sale receipts and labels. The time saved in both setup and operation makes it easier to handle projects efficiently, prompting many businesses or individuals to opt for this particular type of printer. Next, we’ll look at some of the advantages that come along with using a thermal printer in your office or home environment.
Benefits of Thermal Printers

Source: forbes.com
Thermal printers have a number of benefits over their more-traditional counterparts. One of their biggest advantages is the speed and ease of printing. Typically, there are fewer moving parts in thermal printers versus inkjet or laser printer models, creating less periodic maintenance and greater overall reliability. Additionally, since these devices don’t require ink or toner cartridges, they often have a lower upfront cost than other types of printers. In terms of output quality, thermal printers can produce sharp and crisp results due to the high resolution of their printed dots. While other methods may sometimes result in fuzzy images, this isn’t an issue when using a thermal printer. Of course, the lifetime of thermal printouts is generally much shorter than those from inkjet or laser printers. This can be an advantage in certain cases with heat-sensitive labels that regularly need to be updated. In addition to providing users with quick and reliable printing results, thermal printers are known for their low noise production and efficient power usage. With no warm-up period required before printing each item, newer models tend to use very little electricity compared to traditional approaches. All of these attributes provide added value for both businesses and end consumers alike. Thermal printers offer a compact solution without compromising on features or resulting quality. Now that we understand the process behind how these amazing devices work, let’s take a closer look at the different types of thermal printers available on the market today.
Types of Thermal Printers
Thermal printers come in many shapes and sizes, allowing for a range of uses for different tasks. The three types most commonly used are direct thermal, impact, and thermal transfer. Direct thermal printing creates labels or tickets when exposed to heat, eliminating the need for ink or toner cartridges. This method is great for cheaper short-term paper labels because they can fade quickly due to exposure to light, water, and chemicals. Direct thermal printing has other benefits as well; it’s fast and easy to set up and requires minimal maintenance. Impact printing is more durable than direct thermal printing since it does not rely on heat to create prints. Impact technology relies on an array of pins striking against a ribbon or special paper tape to create images or text. Thermal transfer printing also creates extremely durable images with the help of wax or resin-based ribbons instead of ink or toner cartridges. This technology is ideal if you need prints that can survive water contact and last longer than direct thermal prints.No matter what type of thermal printer best meets your needs, they all have advantages over traditional laser or inkjet printers by providing quick, quality prints while eliminating the need for costly replaceable parts such as toner cartridges or large dust collector bins. With greater affordability than non-thermal printers due to its consistent performance and low maintenance needs, paired with their exceptional results, it’s no wonder why thermal printing has become so popular in recent years among businesses everywhere. Knowing what type of printer works best for your particular purposes ensures that you get the most out of your investment – so be sure to weigh all your options before deciding which type of thermal printer is right for you. From cost savings to efficient production times, there’s no denying that thermal printers bring countless advantages over their traditional counterparts. To further explore how setting up a suitable system can bring these benefits even closer to fruition – as well as how to get started – let’s take a look at what goes into getting a comprehensive thermal printer system up and running.
Setting Up a Thermal Printer System

Source: magestore.com
Setting up a thermal printer system is an important step when selecting and using a thermal printer. Depending on the size, scope, and type of project will determine which type of system setup would be most suitable. For example, if you are setting up a simple point-of-sale system with one cash register and one thermal receipt printer then all that is needed is a simple connection between the cash register and the thermal printer. Most standard computers have USB ports so connecting the two devices to the same port should be relatively simple. However, if you need to use multiple thermal printers connected to a large system, then Ethernet networking might be the better option. The benefits of using Ethernet to network multiple printers far outweigh basic USB connections. Ethernet networks can utilize multiple protocols such as TCP/IP, WiFi, and Bluetooth, making them very easily expandable to add more modules and peripherals over time. Furthermore, they provide faster data transfer rates than USB connections so they are better equipped for handling large print jobs quickly and efficiently. When considering the best setup for your system it is important to consider the cost vs benefit ratio. While there may be more expensive options available for setting up an extensive ethernet device network, these will require more complicated configurations, expanding user knowledge and even calling in professional information technology support staff. Therefore, if your thermal printing needs are basic it may not make sense economically to invest in a larger network as an initial investment in the technology. Overall, setting up a thermal printer system will depend on individual needs but understanding the different options available is critical when making decisions about which type of system would best serve your purpose. Careful consideration of cost vs benefit and exploring various protocol compatibility options when configuring your thermal printing system can save time and money while ensuring optimal performance in whatever application you are using it for.
Answers to Frequently Asked Questions with Explanations
What are the advantages of using a thermal printer over a laser printer?
Thermal printers offer a number of advantages over laser printers. First, thermal printers do not require toner or ink which makes them a more cost-effective option in the long run since there are no replacement cartridges needed. Second, thermal printing is much faster than laser printing due to the small amount of time it takes to heat up and print on the ribbon, making it ideal for businesses that need high-volume printing done quickly. Third, thermal printers are able to produce photos and other graphics at a higher quality than laser printers as they do not suffer from dot-banding issues as many laser printers do. Finally, thermal printers require less maintenance than laser printers because all that is needed to maintain the printer are periodic cleaning cycles and replacements of the ribbon which will last significantly longer than typical ink cartridges. All these factors make thermal printers a better choice over laser printers for those who prioritize speed and quality while still trying to keep operating costs low.
What types of documents can be printed with a thermal printer?
Thermal printers are a type of direct thermal printer which utilizes heat to print on special coated thermal paper. They are often used across a variety of industries including retail, hospitality, and logistics due to their ability to quickly and reliably produce printed documents in low volumes. Thermal printers are commonly used to print receipts, barcode labels, wristbands, tickets, and tags. Documents that require high resolution such as photographs or detailed graphics cannot be accurately produced with a thermal printer. However, text-based documents come out crisply, legibly, and with very little downtime for maintenance. With proper care, most thermal printing jobs can last for several years without degradation of print quality.
How do you maintain a thermal printer to keep it functioning properly?
Maintaining a thermal printer is essential for keeping it functioning properly and extending its life. Here are a few best practices to follow:
1. Clean: Regularly clean the parts of the printer with mild soap and water or use an alcohol swab to remove any stuck dust or debris. This will help keep the ink from smearing and ensure that the printing quality remains sharp.
2. Use Quality Consumables: Make sure to always use high-quality toner and paper when printing with your thermal printer. These specially designed materials will ensure optimal performance, color saturation, and durability.
3. Handle With Care: When handling a thermal printer, be sure to take extra care to not damage the printhead. Gently move the printer around and be careful to avoid jarring or dropping it.
4. Avoid Extreme Conditions: Ensure that your thermal printer has enough ventilation and is not being used in overly hot or cold environments for extended periods of time. Ideally, you should store it away from direct sunlight as well, to extend its lifespan as much as possible.
Overall, following these tips can go a long way in helping to maintain a thermal printer so that it continues working properly for years to come!

















